AMD Zen6 Mobile Roadmap Leaks: Up to 24 Cores, 3nm by 2027
A new leak shows AMDS Roadmap for mobile Zen6 processors by 2027. The Gator Range and Medusa series should come with up to 24 cores and 3-nanometer production. What does that mean for the competition for Intel?
Zen6 roadmap for 2027 leaked
AMD is currently riding on a wave of success. The market shares in desktop and server chips are at a record level. The X3D CPUs are particularly successful. According to rumors, more of these processors are already planning with a gigantic cache. A leaked roadmap now reveals AMD’s plans for the next generation of mobile processors.
The first Zen6-based chips are to be released at the end of 2026 to early 2027. The new CPUs aim at high-performance computing and are intended to bring significant improvements in core design and overall performance. The information comes from Leaker @Momomo_us And could stir from an OEM manufacturer who works with AMD. The leaked details show three new series for the mobile market and indicate a fundamental change in AMD’s chiplet architecture.
Zen6 CCDs are to offer (CCD) more than eight cores per core complex for the first time. The number may be increased to twelve or even 16 cores instead of the eight at Zen4 and Zen5. This could lead to up to 24 cores and 48 threads for Ryzen 9 processors.
Gator Range as Fire Range successor
The new Gator Range is to replace the current Fire Range HX series and is aimed at enthusiasts and gamers. These processors will be the first AMD architecture to offer more cores on a single CCD. With up to 24 cores and 48 threads on a TDP from 55 watts, the series positions itself as a desktop replacement for mobile workstations.
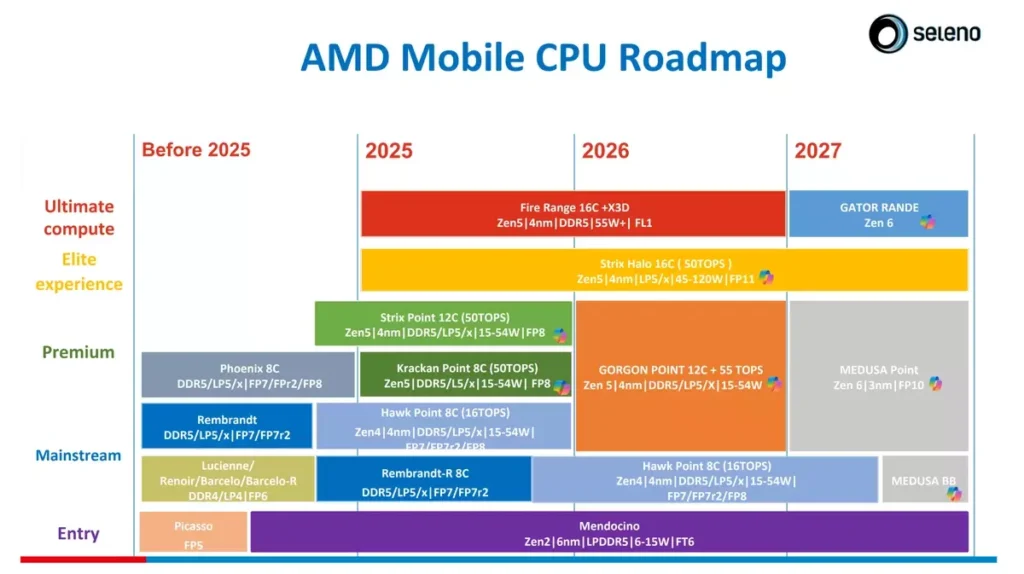
The Medusa series is divided into two variants: Medusa Point for Premium and mainstream markets and Medusa BB for wider consumer segments. Zen6 is expected to use TSMCS 3-nanometer and 2-nanometer processes, which promises a significant increase in efficiency compared to the current 4-nanometer chips.
Medusa Point is said to offer a heterogeneous architecture with Zen6, Zen6c and electricity-saving LP-Zen6 cores. This mixture of performance and efficiency nuclei is similar to Intel’s big.little concept and could help AMD score with both performance and battery life.
Technical innovations and AM5 support
AMD has undertaken to support the AM5 platform by 2027 and beyond. It would be typical of AMD to bring Zen6 to AM5. The company had already introduced several microarchitectures on Socket AM4. This continuity offers users a longer upgrade perspective without changing the mainboard. The Zen6 generation will not only be used in mobile processors.
Desktop processors will appear as a Ryzen 10000 series under the code name “Medusa”, while Epyc server processors are referred to as “Venice”. The Epyc Venice CPUs should offer up to 256 cores, which is more than a doubling compared to the current GenoA processors with 96 cores. The L3 cache sizes should grow proportionally and, in combination with AMDS 3D-V-cache technology, may reach 192 MB or more. For comparison: Current Ryzen-9000x3D processors already offer up to 128 MB L3 cache, which increases gaming performance considerably. Infographic Intel vs. AMD: Ryzen demand in Germany significantly higher
Chiplet design also planned for Apus
It is particularly interesting that AMD could switch from the monolithic design to a chiplet-based approach. The Medusa Point Apus are to combine a Zen6 CCD with twelve cores and a 200 square millimeter I/O-Die with eight RDNA working groups, a 128-bit memory controller and a large NPU. It is speculated that Infinity Cache could be added to improve the GPU performance. This technology, which is already used in AMDS Radeon graphics cards, reduces the dependency on the storage bandwidth and could make integrated graphics solutions much more powerful.
The competition with Intel is further intensifying. While Intel, with its upcoming Arrow Lake and Lunar Lake processors, also relies on new manufacturing technologies, AMD could once again present them technologically with Zen6. AMD’s intentions show the higher number of nuclear number per CCD and the chiplet architecture for Apus to score both with pure computing power and energy efficiency.
Digital marketing enthusiast and industry professional in Digital technologies, Technology News, Mobile phones, software, gadgets with vast experience in the tech industry, I have a keen interest in technology, News breaking.