Common Criteria evaluation: shortly explained

In 2021, 411 IT products and systems were Common Criteria (CC) certified, which means 23 more issued certifications than the year before. But what Common Criteria exactly is? What are the main steps of Common Criteria evaluation and what are the benefits of this certification? Get your answers from our newest article!
What is Common Criteria?
Common Criteria is a framework of internationally acknowledged and scalable standards (ISO 15408) for cybersecurity certification. Common Criteria and its companion, the Common Methodology for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CEM) form the technical foundation for the Common Criteria Recognition Arrangement (CCRA), a global agreement that guarantees:
- Common Criteria evaluation must be performed by an independent and competent accredited laboratory.
- A variety of Certificate Authorizing Schemes can offer certification of an assessed product’s security qualities, based on the results of their evaluation.
- During the Common Criteria evaluation process, supporting documents are used to define how the criteria and evaluation techniques are employed while evaluating and certifying particular technologies.
- These certificates are accepted by all members of CCRA which means currently 31 nations.
What are the main benefits of Common Criteria certification?
It’s crucial to clarify that Common Criteria certification is not chosen for all kinds of IT products and their developers, because of its complexity. The most typically certified products include firewalls, mobile, and network devices, application software, and other particular cybersecurity products. However, the number of issued certificates seems to be increasing every year, as mentioned above, in 2021 only 411 IT products have been CC certified globally.
Common Criteria certification provides multiply benefits:
- Being accepted by all 31 CCRA countries it discharges the disadvantages of duplicated cybersecurity product evaluations and security profiles;
- Guarantees that IT product and security profile evaluations are conducted to consistently high standards, in a rigorous, standard, and repeatable manner.
- The more efficient and cost-effective certification process for IT products and security profiles.
What is Common Criteria Evaluation?
Common Criteria evaluation is the method that an IT product or system has to go through in order to get CC certified.
The Common Criteria evaluation methodology has 3 main elements:
- The official Common Criteria and its supporting documents
- The Common Criteria Evaluation Methodology (CEM)
- A country-specific evaluation methodology is known as an Evaluation Scheme or National Scheme in those countries where there is a Certification Body.
The main elements of Common Criteria evaluation
If you are planning to get your IT product or system CC certified, hiring a Common Criteria expert before starting the process is highly recommended. A carefully selected CC consultant can save a lot of time and energy for any Developer to prepare for the evaluation process following the CC requirements. Besides that, you’ll need to choose a competent and accredited Testing Laboratory that performs the evaluation process.
The IT technology or product that is getting certified is called the Target of Evaluation (TOE). In most Common Criteria evaluation projects of large companies, the Sponsor and Developer of the examined TOE are the same.
There are multiple steps that have to be completed before starting the Common Criteria evaluation. The National Scheme, the TOE, and Protection Profile have been chosen. The latter is optional. Besides the Security Target and Evaluation Work Plan have to be prepared. And last but not least the Evaluation Assurance Level has to be picked.
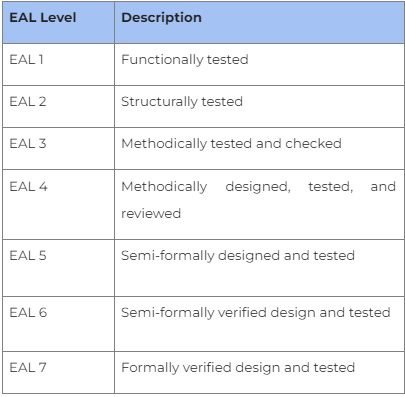
What are Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance Levels?
Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) represents how comprehensively an IT security product or system is tested. EALs range from 1 to 7, with 1 being the lowest degree of evaluation and 7 defining the highest level. It’s important to know that a higher-level rating does not necessarily mean that the product is more secure; rather, it suggests that the product has undergone deeper or more assessments.
The length of the Common Criteria evaluation process depends on numerous factors, for instance, the product’s complexity or the picked EAL. Generally, it takes up to a few months, but it can be much longer depending on the quality of the Developer documents and the readiness of the Sponsor/Developer. Once the process is completed the Laboratory issues the Evaluation Technical Report (ETR) to the Certification Body, which will be the basis of the later issued certificate.
How does the Common Criteria evaluation process end?
As the Common Criteria evaluation is completed by the issued ETR, the next step of the process is that the Certification Body(CB) issues a draft Certification Report (CR) roughly in 30 days. The draft is being sent to the Test Laboratory and the Sponsor to get their approval. Approximately 30 days after the draft gets approved by both parties, CB issues the Certification Report and – in case of successful evaluation – adds the Certificate to it. This issued Certification is valid only to the specific version of the TOE in its evaluated configuration and declares that the chosen EAL has been accomplished.
Alexia is the author at Research Snipers covering all technology news including Google, Apple, Android, Xiaomi, Huawei, Samsung News, and More.