How to Make Your Website Understandable to LLMs

Not long ago, websites were built for people first and search engines second. In 2025, they need to be built for three audiences at once: humans, search engines, and AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude.
Whether audiences realize it or not, more people are now discovering brands through AI summaries. They ask ChatGPT for the “best CRM for small teams,” “how to start a consulting business,” or “alternatives to WordPress,” and more trust in the model’s reasoning is growing as users grow their trust in the new technology.
AI-driven discovery has quietly become its own search layer that rewards clarity, structure, and semantic accuracy. The challenge is that models can only recommend or summarize information they clearly understand.
If your website isn’t written and structured for machine logic, AI may misinterpret it, omit it, or fail to reference it entirely.
The solution is surprisingly simple: make your website easy for machines to read, interpret, and summarize. Coincidentally, making your site machine-ready also makes it more accessible to human users.
Write for Understanding, Not Performance
The biggest misconception about AI optimization is that it’s too technical. In reality, the most important factor is plain-language clarity. Large language models interpret writing the same way humans do. They look for context, logic, and cohesion.
If your website is filled with jargon, vague claims, or clever-but-ambiguous copy, AI won’t interpret it correctly.
Compare these two statements:
Vague marketing copy: “We empower businesses through cutting-edge digital solutions.”
Machine-friendly clarity: “We design and develop websites for businesses, specializing in UX, Webflow development, and SEO.”
The first line is “brand voice.” The second line is understandable. Models (and people) prefer the latter.
Good AI optimization looks a lot like good communication.
Use Clear Structure: Headings Are Meaning Signals
Headings aren’t just formatting, they’re semantic markers that teach AI how your site is organized.
A model will interpret:
- H1 = the page’s core meaning
- H2s = major themes
- H3s = supporting details
When headings are inconsistent, missing, or decorative, AI struggles to interpret the hierarchy of information.
For example:
Unclear for AI
A page with three H1 tags
Section titles that are styled visually but not semantically
Headings that don’t match the content below them
Clear for AI
A single descriptive H1
Clear H2s for each major section
Consistent H3s for steps, lists, or supporting content
Headings that describe exactly what users will learn
AI models use these cues to answer questions like:
- “Who is this company?”
- “What exactly do they offer?”
- “Is this page relevant to the query asked?”
Clarity = comprehension.
Use Semantic HTML So AI Knows What’s What
Semantic HTML helps machines understand the role of content.
It lets AI distinguish between:
- navigation vs. content
- headers vs. metadata
- sidebars vs. main text
- blog posts vs. product pages
Pages built purely with <div> elements are visually fine, but structurally opaque.
You don’t need to rebuild your site to fix this. Even small semantic improvements increase interpretability.
Use:
- <header>
- <main>
- <footer>
- <article>
- <section>
- <nav>
- <aside>
- <h1>–<h3>
These tags become metadata for AI, helping the model understand relationships and context. Good semantic structure is accessibility, SEO, and AI optimization bundled into one.
Build Content That Explains Itself (Even When Quoted Out of Context)
AI models often summarize, paraphrase, or extract sections of your content. That means each block of text should function as a standalone statement.
For example:
Not AI-friendly: “These three tools work well together.”
This sentence doesn’t clarify which tools, why, or how. If quoted independently, it’s meaningless.
AI-friendly: “These three tools — analytics, heatmaps, and AI-generated insights — work well together because they show what users do, where they hesitate, and why they convert.”
This line functions even if an AI extracts it alone. Models reward specificity, clarity, and self-contained meaning.
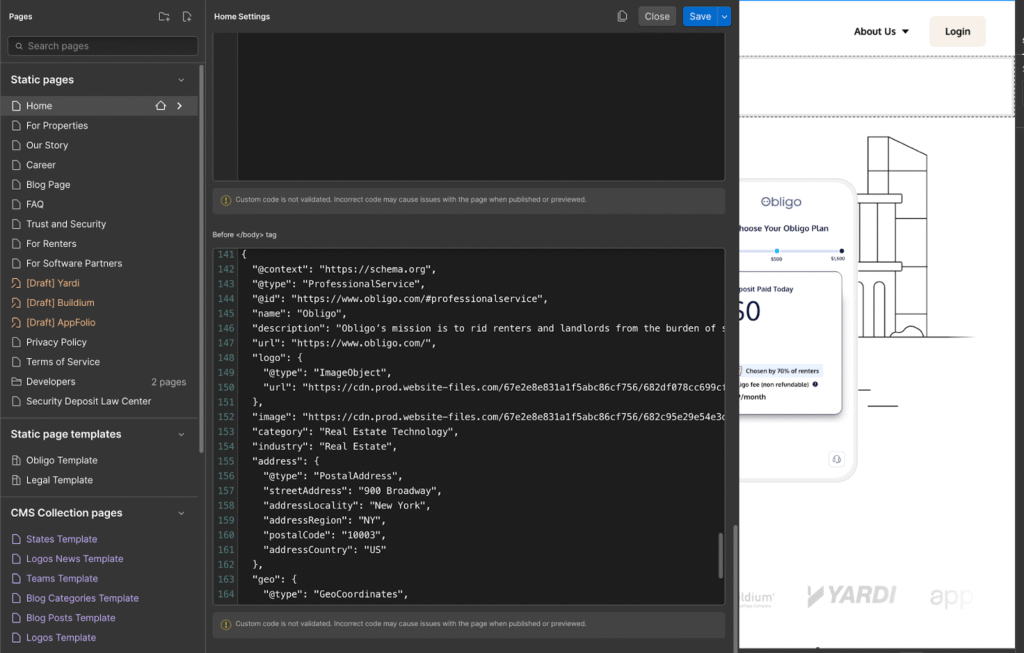
Add Schema Markup: The Machine-Readable Version of Your Brand
Schema markup is structured data embedded in your website. Humans don’t see it, but machines rely on it.
Schema tells AI:
- who you are
- what you do
- where you operate
- whether you’re credible
- how pages relate to each other
For example, an Organization schema might include:
- business name
- description
- address
- social profiles
- founder
- logo
- contact information
This clarity becomes part of your “machine identity.” It’s the difference between AI guessing what you do and knowing what you do. Search engines already use schema to power rich results. LLMs now use it to understand brands in a structured, factual way.
Use Consistent Language Across All Platforms
If your website says you’re a design agency, your LinkedIn says you’re a SaaS tool, and a random directory lists you as an eCommerce founder, AI gets confused.
LLMs build “entity graphs” from scattered data across the web. Inconsistency fragments how your brand is interpreted.
To improve consistency:
- Use the same high-level description everywhere.
- Keep your offerings listed similarly across channels.
- Describe your niche with the same phrasing.
- Update outdated bios and profiles.
Consistency isn’t branding, it’s visibility. AI can only recommend what it understands with certainty.
Increase Accessibility: What’s Clear for Users Is Clear for AI
Accessibility and AI optimization overlap significantly. Screen readers and LLMs both rely on:
- proper heading structure
- semantic HTML
- alt text
- ARIA labels
- predictable navigation
- descriptive link labels
- readable contrast
When a website is accessible, it’s also machine-friendly. If a screen reader can interpret your site, so can an AI model.
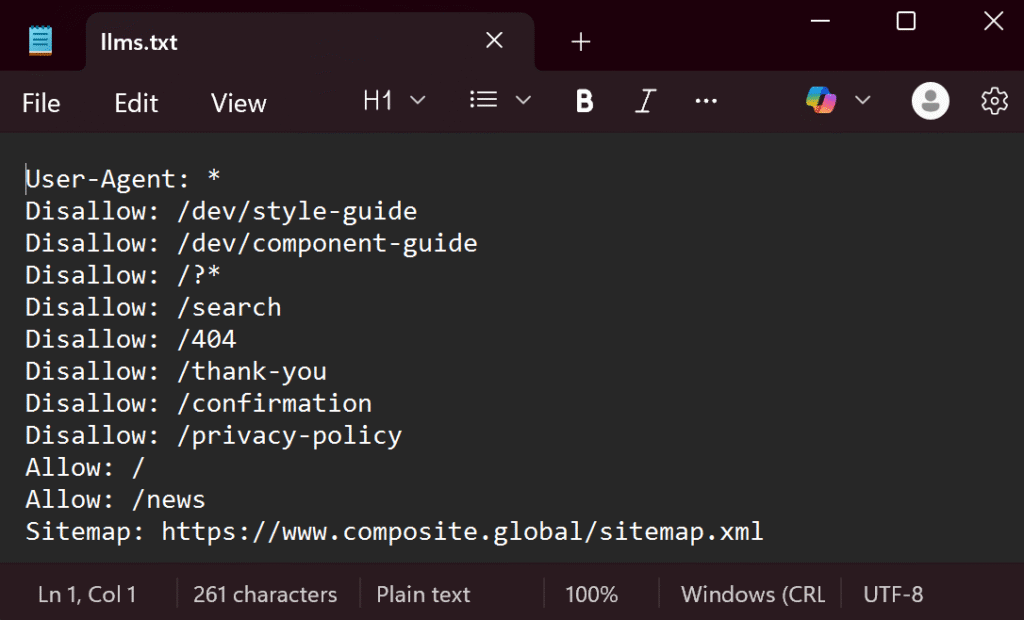
Add an llms.txt File (An Emerging Best Practice)
There’s a growing movement toward adding an llms.txt file, an experimental mechanism for telling AI models how they may use your content. It’s similar to robots.txt, but for LLMs.
You can specify:
- which AI crawlers you allow
- which directories they can read
- which content is off-limits
- whether your data can be used for training
- Which content to prioritize
This isn’t universally adopted yet, but early adopters signal transparency and control. For a deeper explanation of how this protocol works, see SEO for ChatGPT: Help LLMs Understand Your Website.
Even if all models don’t fully support it yet, llms.txt is positioning your brand for the next era of AI governance.
Make Your Navigation Predictable
AI models infer meaning from your site architecture. If navigation is unconventional or overloaded with clever labels, models (and users) misinterpret your structure.
Good AI-friendly navigation:
- uses simple, descriptive labels
- groups content logically
- avoids “mystery meat” navigation
- minimizes deep nesting when possible
Clear navigation helps AI map your topics accurately, improving both visibility and summarization.
Treat Clarity as a Ranking Factor
AI-driven discovery isn’t about keywords. It’s about meaning. Future visibility depends on:
- how well your content explains itself
- how clearly your structure communicates relationships
- how consistently your brand describes itself
- how readable your site is to machines and people
Clarity is the new SEO. And unlike algorithms, clarity benefits everyone: your team, your customers, and the AI systems that increasingly act as your intermediaries.
Looking Forward
Optimizing for AI isn’t technical, it’s foundational. It means building websites that are clear, accessible, structured, and self-explanatory.
When your site is easy for machines to understand, it becomes easier for people to find.
When your meaning is unambiguous, it becomes easier for AI models to recommend, summarize, and reference.
AI isn’t replacing search, it’s adding a new layer of discovery. The businesses that embrace this shift early will own the next generation of visibility.
Alexia is the author at Research Snipers covering all technology news including Google, Apple, Android, Xiaomi, Huawei, Samsung News, and More.












