Vulnerabilities found in TPM 2.0 reference implementation
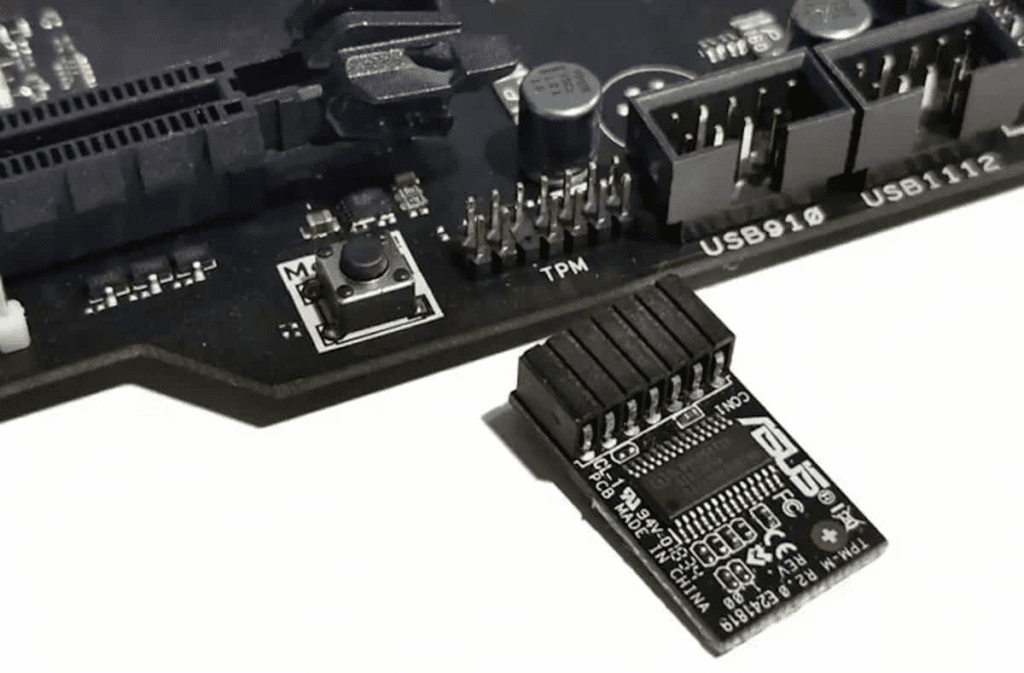
Flaws in the specification of the TPM 2.0 reference implementation make some security modules vulnerable to hackers. Arbitrary code can be executed through incorrectly processed parameters. The problem probably affects only a few manufacturers.
Quarkslab security researchers have discovered two vulnerabilities in the context of processing some parameters of TPM commands. The errors can be found in the TPM library specification “Session-based encryption” and the reference implementation based on it as The Hacker News reported. A function may access memory areas outside the intended limits. The vulnerabilities are known as CVE-2023-1017 and CVE-2023-1018.
Hackers can push malicious code
The bug gives attackers the option to send manipulated commands to the security chip. Here, the data stored in the memory of the module can be read out. Protected data can also be overwritten, allowing code to be injected into the TPM. However, the attack requires that the hacker already has local access to the system.
The relevant parts of the specification have now been updated so that TPM providers can fix the vulnerabilities. Both manufacturers and users should install all available updates as soon as possible. In many cases, an update of the security chip requires that the TPMs be reset to the factory settings. Of course, the saved keys will be lost in the process.
It is still unclear which operating systems are affected by the bug. The security chips are supported by 1608 vendors. The assessment so far has shown that the software of 142 organizations is not vulnerable. It is currently only known that six providers are affected. These are NixOS, Red Hat, Squid, SUSE Linux, libtpms, and the Trusted Computing Group.
Digital marketing enthusiast and industry professional in Digital technologies, Technology News, Mobile phones, software, gadgets with vast experience in the tech industry, I have a keen interest in technology, News breaking.